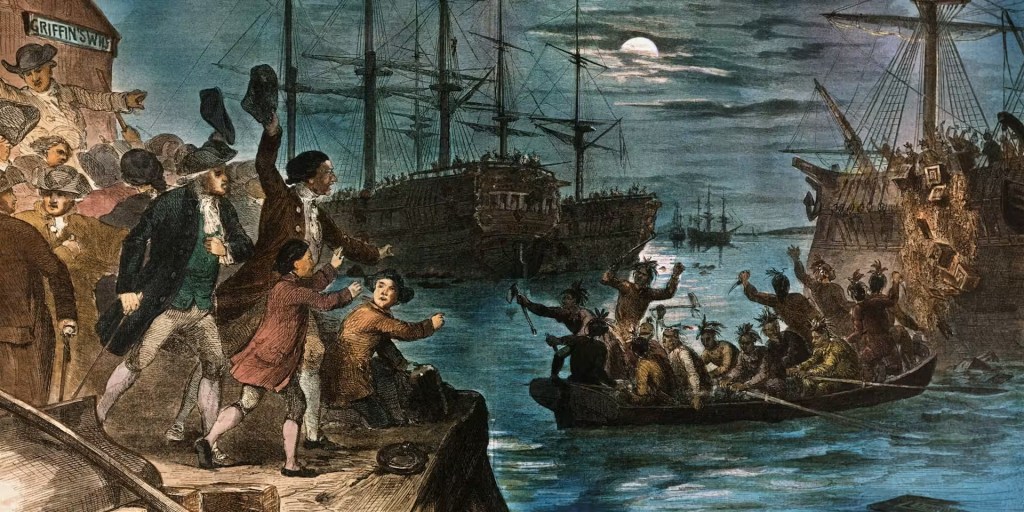
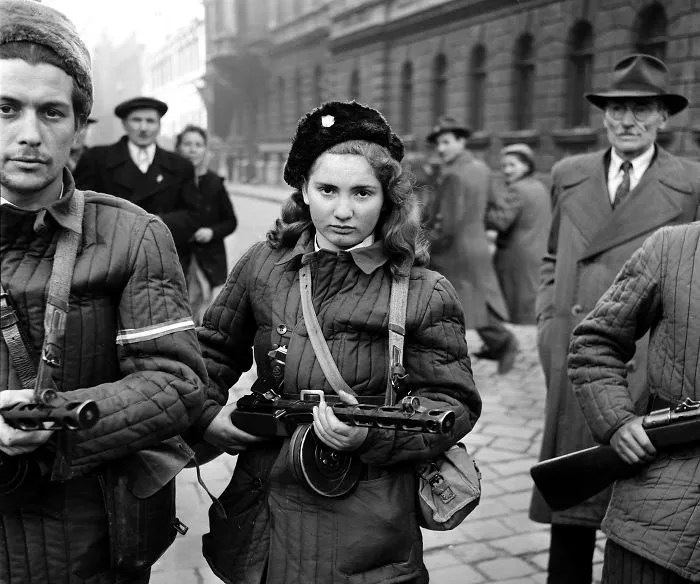
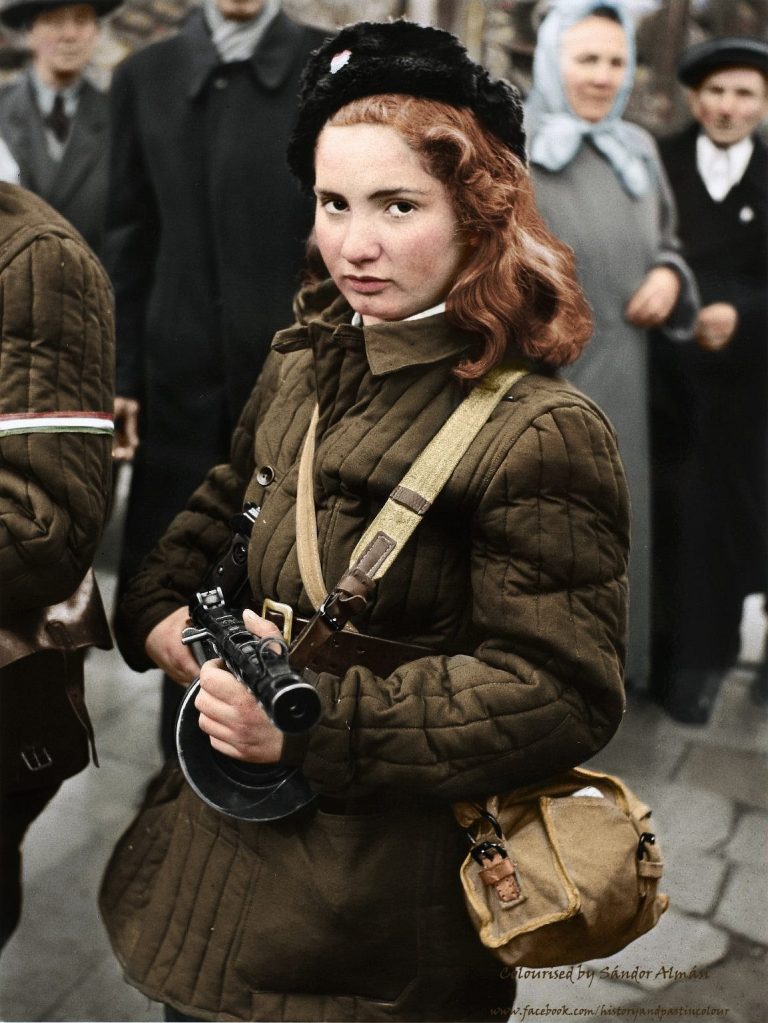
On the night of December 16, 1773, over 100 Bostonians disguised as Mohawk or Narragansett warriors boarded three merchant ships of the British East India Company moored at Griffin’s Wharf in Boston Harbor and proceeded to dump 342 chests of tea overboard in what would become known as the Boston Tea Party. It was organized and carried out by the Sons of Liberty—a secretive organization led by Samuel Adams and John Hancock—who were the driving force of opposition to British rule over the colonies. The tea party was an act of protest driven by long standing colonial grievances against British rule but the primary complaint was the Tea Act of 1773 and the fact that the American colonies were taxed as subjects of the British crown but denied representation in Parliament. The tea party set off a series of British punitive measures known as the “Coercive” or “Intolerable” Acts that eventually plunged New England and the remaining American Colonies into armed rebellion against British rule two years later.
In the decade prior to the tea party, Great Britain was facing serious economic difficulties. It emerged victorious from a seven year struggle against arch rival France in 1763, known as the French and Indian War in North America, but its treasury was depleted. Moreover, the British economy was mired in a recession as a result of policies that were implemented to finance the war. The British government looked for new and untapped means to replenish its coffers and beginning in 1764 it levied a series of new taxes and customs duties on the American Colonies to raise more revenues. Over the next, eight years the British Parliament in London passed the Sugar Act, Stamp Act, and the Townshend Acts, provoking violent protests by the outraged colonists.
The colonist anger stemmed from a deep seated conviction that the power to tax derived from the consent of the governed, a principle dating back to 1215 and the Magna Carta. The colonists were already paying taxes levied by their colonial legislatures for public goods and services and since there was no colonial representation in parliament, they argued, London had no right to impose additional taxes and duties on the colonies. British authorities disagreed. As such, the brewing crisis was not simply about taxes but about the power relationship between Great Britain and the colonies.
By the 1770s, relations between the American colonist and the British government had become increasingly acrimonious, if not confrontational, with Boston serving as ground zero for all anti-British sentiment and protests. In March 1770, British troops, who had been deployed to Boston earlier to quell violent protests over the Townshend Acts, opened fire on a small group of angry Bostonians, who had been heckling them, killing five in what would become known as the Boston Massacre. The massacre only served to further roil an already indignant public. In May 1773, the British Parliament passed the Tea Act which was intended to help the East India Company, one of Britain’s most important commercial institutions, stave off financial ruin and reassert its authority over the increasingly rebellious American colonies.
The Tea Act was a complex plan that actually lowered the price of tea but it also forced the colonists to pay a tax of three pence on every pound of tea while granting the East India Company a monopoly on the tea market in the colonies. Many colonists denounced the act, seeing through it for what it was, a ruse to make them accept Parliament’s right to tax them. Moreover, the act threatened to put smugglers and legitimate importers out of business because it undercut the price of tea that smugglers were offering and the tea had to be purchased from designated consignees. As a result a nexus of opposition emerged to include radical political activists, smugglers, and the merchant class.

The first tea ships of the East India Company began to reach North America in November of 1773. Seven ships were bound for Boston, New York, Philadelphia and Charleston. The ships encountered strong opposition in all four cities and in New York, Philadelphia, and Charleston the ships were prevented from unloading their cargo and forced to return home. In Boston, a defiant Royal Governor, Thomas Hutchinson, was determined to assert his authority demanded that the ships be allowed to dock and that colonial merchants pay the duties on the cargo. On 28 November, the Dartmouth, arrived in Boston Harbor. It was soon joined by two other ships, the Eleanor and the Beaver. Threats from the Sons of Liberty and other like-minded groups prevented the ships from unloading their tea while Hutchinson would not allow the ship to leave the port without the customs duties being paid. The stage was set for a historical showdown.
On the afternoon of December 16, nearly 5,000 Bostonians crammed into the Old South Meeting house to listen to Samuel Adams, John Hancock, and others debate a course of action to resolve the tea crisis. Late in the day, word spread that a last ditch effort to persuade Hutchinson to send the ships back had failed. Frustrated by the impasse Adams concluded, “This meeting can do nothing more to save the country!” With those words the meeting came to an abrupt close, and it was the signal for the Sons of Liberty to carry out a more radical plan, one which they had been preparing for for some time.
As the people filed out of the Old South Meeting House, a mob began to form and shouts of “Boston Harbor, a teapot tonight!” filled the air. The mob made its way towards Griffin’s Wharf where the three ships of the East India Company were moored. Along the way, 150 Sons of Liberty donned disguises as Mohawk and Narragansett warriors to conceal their identities and avoid any future retribution for acts they were about to carry out. The affair was planned and executed meticulously. The mob boarded the ships roughly around 7pm under a cover of darkness meeting little resistance from the ships’ crews. They proceeded to pry or smash open the 342 tea chests dumping their contents overboard into harbor. The conspirators were careful to ensure that no other property or people were vandalized or harmed or that anyone from within their ranks stole any of the tea. After three hours of heated work, they dispersed from the ships and returned to their homes, with each man having sworn an oath of secrecy about the affair.
Word of the tea party reached London little over a month later prompting a strong response from the British Government. British Prime Minister Lord North was determined to reassert British authority over the rebellious colonists and teach them a lesson they would not forget. In March 1774, British Parliament passed the first of a series of measures known as the “Intolerable Acts” intended to punish the colonists for their tea escapade. The first measure was the Boston Port Act which authorized the Royal Navy to blockade Boston, effectively shutting down the port to almost all commerce and trade until the tea was paid for. The port closure halted virtually all maritime trade, causing massive job losses, shuttered businesses, and created a humanitarian crisis as food supplies became scarce. The second, which was passed in May, was the Massachusetts Governing Act which ended the Massachusetts Constitution and the free election of local officials. Instead, it gave the Royal Governor the power to appoint local officials which posed a direct threat to representative government in the colony. On the same day, parliament also approved the Act for the Impartial Administration of Justice which gave the governor the ability to move a trial to another colony or Great Britain if it is determined “that an indifferent trial cannot be had within the said province.” The Act eliminated the right to a fair trial by one’s peers, removing an established judicial principle dating to Magna Carta. The fourth and final punitive measure was the Quartering Act passed in June which obligated the colonist to pay for housing British soldiers in North America. Lastly, Parliament wanted someone with a stronger hand to implement these acts and replaced Thomas Hutchinson with General Thomas Gage as Governor of Massachusetts, effectively putting the colony under military rule. In addition to serving as Royal Governor, Gage was also Commander-in-Chief of British forces in America. Gage and four fresh regiments set sail for Boston in mid-April 1774.
It was the fervent hope of the Crown that these strict and punitive acts would serve as punishment for the colony of Massachusetts and as a warning and threat to the other American colonies as well. The calculation was that other colonies would soon submit to British authority and resume their place as subordinates to Parliament and the Crown out of fear of similar reprisals.
However, these measures backfired on the British. Other colonies recoiled in horror at what they witnessed. After seeing the power Great Britain leveled on Massachusetts, other colonies quickly became sympathetic with their fellow colonists and began to wonder how much longer it would be before the same type of actions would be done to their own cities or colonies. The other American colonies soon sent aid and supplies to the beleaguered people of Boston.
On top of the fear these acts caused in colonies throughout America, they also forced the colonists to begin asking more important questions. These questions included: where had Great Britain received its authority? And to what degree did they have the right to use such force on the colonies? The word tyranny was used to describe the actions of Parliament and the Crown. Men like George Washington in Virginia would write, “Shall we supinely sit, and see one province after another fall a sacrifice to despotism?” In a years time, “the shot heard around the world” would ring out on Lexington green marking the beginning of the American Revolution.