
On August 23, 1939, Soviet Foreign Minister Vyacheslav Molotov and German Foreign Minister Joachim von Ribbentrop signed the notorious Nazi-Soviet Non-Aggression Pact paving the way for Hitler to invade Poland and precipitating what would become World War II. Under the terms of the agreement, Nazi Germany and the Soviet Union agreed to refrain from any military aggression against each other for a period of ten years. The agreement also included a secret protocol partitioning Poland and dividing Central and Eastern Europe into “spheres of influence.” The pact was a cynical gambit between two seemingly implacable ideological foes that allowed Hitler to invade Poland without fear of becoming caught up in a two-front war. For Soviet leader Josef Stalin it was a calculated gamble to delay an almost inevitable German attack on the Soviet Union and regain territories lost during the Russian Revolution, Civil War, and the 1920 Polish- Soviet War.
German tanks and aircraft brutally attacked Poland in blitzkrieg fashion on September 1, 1939, crushing all resistance from the brave but antiquated Polish military. On September 17, the Soviet Red Army entered Poland from the East, as stipulated in the Molotov-Von Ribbentrop Pact, effectively partitioning Poland out of existence. Stalin would justify the entrance of Soviet troops into Poland as a necessary security measure to protect Poland’s Belarusian and Ukrainian minorities. However, Stalin held more insidious ambitions. Hundreds of NKVD secret police officials followed in the footsteps of the Red Army. Their mission was to organize sham referenda in which the Belarusian and Ukrainian minorities of eastern Poland would petition to join the Soviet Union and root out any opposition to Soviet rule. By November, the Soviet Union annexed all Polish territory it occupied. Some 13.5 million Polish citizens suddenly became Soviet subjects following bogus referenda conducted in an atmosphere of terror and intimidation. The NKVD subsequently carried out a campaign of political violence and repression targeting Polish authority figures, such as military officers, police and priests for arrests and execution. Hundreds of thousands of people would be deported from eastern Poland to Siberia and other remote parts of the Soviet Union between 1939 and 1941.
The Soviets would repeat a similar script the following summer regarding the three Baltic States of Lithuania, Latvia, and Estonia. According to the terms of the Molotov-von Ribbentrop Pact the Baltic States were consigned to a Soviet sphere of influence. These three states had been reluctant components of the Russian Empire prior to World War I but emerged from its wreckage as independent states afterward. In the fall of 1939, Stalin coerced the Baltic States into signing mutual assistance treaties with the USSR after invading Poland from the East. These treaties allowed the Soviets to establish military bases in these countries and deploy up to 30,000 troops in each state. Moscow claimed that a Soviet military presence was necessary to protect Lithuania, Latvia, and Estonia from attacks by Nazi Germany. In June 1940, Stalin falsely accused the Baltic States of engaging in anti-Soviet conspiracies and issued an ultimatum to Lithuania demanding that additional Soviet troops be allowed to enter Lithuania and that a new pro-Soviet Lithuanian government be formed. Similar ultimatums were issued to Latvia and Estonia within days. The Red Army subsequently occupied Lithuania on 15 June, Latvia on 16 June, and Estonia on 17 June.
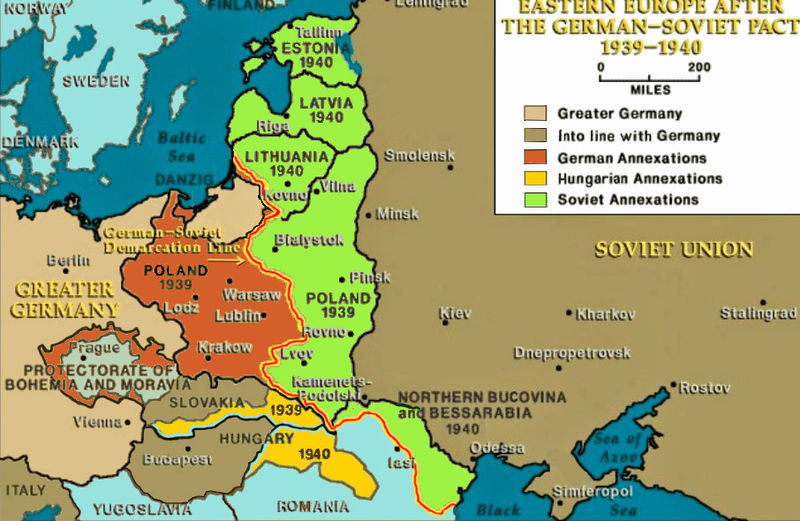
Over the next month, NKVD operatives poured into the Baltic States and began preparations for bogus elections to form new pro-Soviet governments. Between July 21-23, these new puppet governments declared themselves Soviet Socialist Republics and issued a “request” to be incorporated into the USSR. On August 3, Lithuania became the first Baltic State to be absorbed into the Soviet Union followed by Latvia and Estonia. Much like eastern Poland, the Baltic States were subject to an extreme policy of Sovietization, including arrests, executions and mass deportations. These terror tactics continued into the post-war period as agriculture in the Baltic States was collectivized and resistance to Soviet rule increased. More than 300,000 people from Estonia, Latvia and Lithuania would be deported to remote areas of the Soviet Union by the 1950s. Following the end of World War II, the Red Army waged a decade long counterinsurgency against Lithuanian partisans known as the “Forrest Brothers,” resisting Sovietization.
Stalin’s final territorial conquests as part of Molotov-von Ribbentrop were the Romanian provinces of Bessarabia (modern day Moldova) and Northern Bukovina (part of Ukraine). Throughout the 19th century ownership of Bessarabia shifted back and forth between the Russian and Ottoman Empires in a series of wars. In January 1918, Romanian military forces marched into Bessarabia, seizing the province from the Bolsheviks amidst the chaos of the Russian Civil War. The Bolsheviks never forgot the Romanians perfidy. On 26 June 1940, Soviet Foreign Minister Molotov sent an ultimatum to the Romanian government demanding the evacuation of the Romanian military and civil administration from Bessarabia and the northern part of Bukovina or risk way with the Soviet Union. Reluctant to give in to Soviet demands, the Romanians turned to their Nazi allies in Berlin for advice and protection. Berlin advised Bucharest to appease the Soviets and on June 28 Soviet military forces began entering Bessarabia unopposed. One month later the Moldavian Soviet Socialist Republic was proclaimed on August 2, 1940.
The Soviets consistently defended Stalin’s decision to sign a non-aggression pact with Hitler as a correct and necessary measure to ensure the security of the Soviet Union, given the suspect nature of the security guarantees Great Britain and France were offering. For years the Soviets also denied the existence of any secret protocols in the Molotov-von Ribbentrop Pact and claimed that the Baltic States were incorporated into the Soviet Union at their own request. The United States never officially recognized the Soviet annexation of the Baltic States and for years up until the collapse of the Soviet Union, there were Lithuanian, Latvian and Estonian embassies on 16th street in Washington DC.
In August 1989, Soviet leader Mikhail Gorbachev finally acknowledged the existence of the Molotov-Von Ribbentrop Pact’s secret protocols and that Nazi Germany and the Soviet Union illegally divided up parts of Eastern Europe into spheres of influence before the start of World War II. It was an ill-conceived plan intended to placate the Baltic Republics and quell their growing demands for greater autonomy and independence. However it did little of the sort because Gorbachev stopped short of admitting that the Baltic States were forcibly incorporated into the Soviet Union. On August 23, 1989, the 50th anniversary of the pact, over one million people created a 400 mile human chain linking Estonia, Latvia and Lithuania in a symbol of solidarity and a call for a restoration of their independence and statehood.
Russian President Putin has subsequently walked back Gorbachev’s admission, amidst an overall down turn in relations with the West since 2014. Putin has denounced what he considers Western attempts to rewrite history by transferring blame for unleashing World War II from the Nazis to the Soviet Union. Putin has defended the pact as a necessary realpolitik choice made by Stalin under challenging circumstances while rehashing old Soviet disinformation that the Baltic States joined the Soviet Union of their own free will. Lastly, he has tried to recast Poland not as an innocent victim of Nazi-Soviet treachery but as the architect of many of its misfortunes, noting that Poland illegally annexed Czechoslovakian territory following the Munich Conference.
.



